A Computer System is a combination of various components that perform multiple tasks.
The components of a computer system include hardware, software, data, and users.
Block Diagram of Computer System
A block diagram of a computer system is the graphical representation of the main components and their interactions.
It can help to visualize how a computer works.
 |
| Block Diagram of Computer System |
Also, it helps to understand a computer's basic structure and functions, as well as the flow of data and instructions between the hardware and software.
It illustrates the entire process, starting from collecting input data, then proceeding to process and format it, and finally generating the output results in the way the user commands.
Input Unit
This is where the user provides the data and commands to the computer through devices such as a keyboard, mouse, scanner, etc.
The input unit converts the data into binary form and sends it to the storage unit.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU, also known as the Central Processing Unit, is the brain of a computer system.
It comprises several key components that work together to carry out the instructions of a computer program.
- Memory Unit
The Memory Unit refers to the storage component of the computer that stores data and instructions that the CPU needs to access and process.
While the CPU handles the processing tasks, the Memory Unit provides the necessary storage space for the CPU to retrieve and store data.
Together, these two components work in harmony to ensure the smooth functioning of a computer system.
- Control Unit
The most important component of the CPU is the Control Unit.
It plays a crucial role in managing and coordinating the operations of the CPU.
Furthermore, the Control Unit is responsible for fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, and executing them by sending signals to other CPU parts.
Additionally, the Control Unit ensures that all tasks are carried out in the correct sequence and coordinates the data flow between different components.
The CPU could not operate properly or efficiently without the Control Unit.
- Arithmetic and Logical unit
The CPU is responsible for carrying out arithmetic and logical operations within a computer system.
The Arithmetic Unit handles mathematical calculations such as addition and subtraction, whereas the Logical Unit performs logical operations like comparisons and data manipulation.
Output Unit
This is where the computer displays the processing results to the user through devices such as a monitor, printer, speaker, etc.
The output unit converts the data from the binary form to a human-readable form and sends it to the output device.
Components of Computer System
Different components of the computer system are divided into two parts:
Internal Components
The central processing unit (CPU), the computer system's brain, executes instructions.
Since it handles the majority of computations, the CPU is the most crucial part of a computer.
- Memory
The memory of a computer system is where the CPU can access data and instructions.
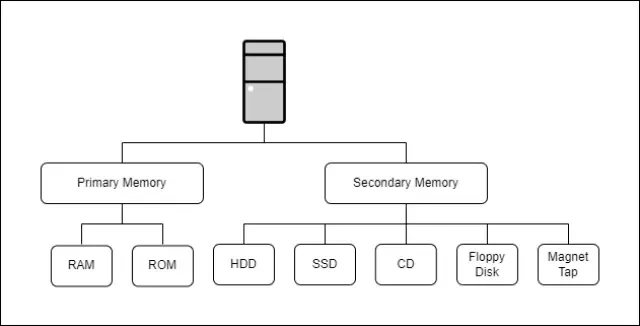 |
| Types of Memory in Computer Systems |
Memory classification helps to understand how data is stored, accessed, and processed within a computer system.
Some common types of memory in computer systems include Primary Memory and Secondary Memory.
Primary Memory is volatile memory that is used to store data temporarily such as:
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Secondary Memory is non-volatile memory used to store permanent data such as:
- Hard Drives Disk (HDD)
- Solid-State Drives (SSD)
- Compact Disks (CD)
- Floppy Disks
- Magnet Tap
Hard drives use spinning disks to store data, while solid-state drives use memory chips.
We can connect an external storage device to the computer through USB or other interfaces.
The storage determines the amount of data that can be stored and the speed at which it can be accessed, making it an essential component.
- Control Unit
The motherboard is the main circuit board in a computer; it is responsible for connecting and controlling all of the internal components.
Additionally, it contains the CPU socket, memory slots, and various ports and connectors.
It also contains the BIOS (basic input/output system), which controls the basic functions of the computer.
Making sure that all of the computer's components effectively communicate with one another is the job of the motherboard, which acts as the computer's brain.
- Arithmetic and Logic unit
This unit is for calculating and performing arithmetic and logical operations in computers.
Arithmetic operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division, and logical operations like and, or, less than, greater than, etc.
External Components
A computer system consists not only of internal and external components that play an essential role in its functionality.
These components include input/output, peripherals, and external storage devices.
- Input / Output Devices
Input-output devices facilitate data transfer between the computer and the outside world.
In terms of input, devices such as a keyboard, mouse, and microphone are used to enter data or issue commands for executing operations.
On the other hand, output devices, including monitors, speakers, and printers, play a crucial role in presenting information to the user.
These gadgets enable users to interact with the computer, performing actions such as typing, clicking, and listening to audio.
- Peripherals
Peripheries are additional devices that connect to a computer to enhance its functionality.
These include devices such as printers, scanners, and webcams.
These devices enable extra features like document printing, image scanning, and video conferencing.
- External Storage Devices
An external storage device stores a large amount of data outside of the computer.
These include external hard drives and USB flash drives.
These tools are useful for transferring files between computers and backing up crucial data.
Another external component of the computer system is the Network Interface Card (NIC) or Network Adapter.
This allows the computer to connect to a network, either wired or wirelessly.
It enables file sharing, internet access, and computer-to-computer communication.
Conclusion
A computer system is a combination of hardware and software that work together to perform various tasks.
It consists of components such as input/output devices, the central processing unit (CPU), memory, and output units.
The block diagram of a computer system helps visualize the structure and flow of data and instructions between the hardware and software.
Additionally, the computer system includes internal components like the memory, control unit, and arithmetic and logic unit, as well as external components like input/output devices, peripherals, and external storage devices.
Comments
Post a Comment